

Yajnik, M., Moon, S., Kurose, J., & Towsley, D. Network Working Group Request for Comments, no. A conservative selective acknowledgment (SACK)-based loss recovery algorithm for TCP. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 8(2), 133–145.īlanton, E., Allman, M., Fall, K., & Wang, L. Modeling TCP Reno performance: A simple model and its empirical validation.

TCP/IP illustrated, vol. 2: the implementation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 11(6), 959–971. Analytic models for the latency and steady-state throughput of TCP Tahoe, Reno, and SACK. Sikdar, B., Kalyanaraman, S., & Vastola, K. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 11(3), 370–383. Comparative study of various TCP versions over a wireless link with correlated losses. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5, 1526–1536.Īnjum, F., & Tassulas, L. SR ARQ delay statistics on N-state Markov channels with non-instantaneous feedback. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4, 1858–1868. On the delay statistics of SR ARQ over Markov channels with finite round-trip delay. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 52, 1365–1377. Analysis and heuristics for the characterization of selective repeat ARQ delay statistics over wireless channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 49(5), 1968–1981. Delay analysis of selective repeat ARQ for a Markovian source over a wireless channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 35, 166–173. Resequencing delay and buffer occupancy under the selective-repeat ARQ. of NPDPA 2002 (2002 IASTED international conference on networks, parallel and distributed processing, and applications) (pp. Comparative performance analysis of basic window size adjustment algorithms for dynamic-window flow control in interconnected network environments. Analysis of link-level hybrid FEC/ARQ-SR for wireless links and long-lived TCP traffic. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4(3), 1017–1029.īarakat, C., & Fawal, A. Delay analysis of selective-repeat ARQ with applications to link adaptation in wireless packet data systems.
Luo, W., Balachandran, K., Nanda, S., & Chang, K.

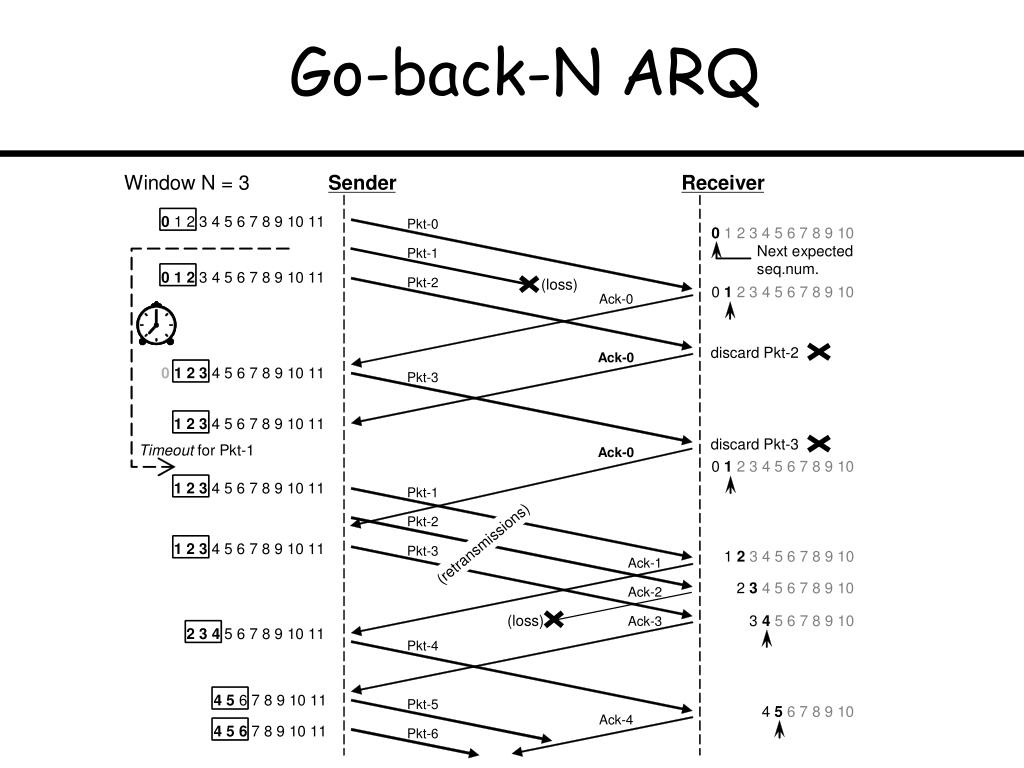
Technical specification group radio access network Radio link control (RLC) protocol specification. ACM Computer Communication Review, 35(2), 37–52.ģrd Generation Partnership Project. Measuring the evolution of transport protocols in the Internet. Mathis, M., Mahdavi, J., Floyd, S., & Romanow, A. High Performance TCP/IP networking: concepts, issues, and solutions. The transport layer: tutorial and survey. IEEE Communication Magazine, 22(12), 5–17. Automatic-repeat-request error-control schemes. Improving TCP performance over mobile networks. A survey of light-weight transport protocols for high-speed networks. A., Dykeman, D., Kaiserwerth, M., Meister, B. Furthermore, we show that the SR-SWP model exhibits the lower goodput and the smaller mean resequencing delay than those obtained from the traditional SR-ARQ protocol model.ĭoeringer, W. From numerical results, we demonstrate that the impact of TORE on the performance is not negligible for high packet-loss probabilities. Using this model, we derive explicit forms of goodput and mean resequencing delay, which are fundamental qualities of service parameters. We propose an analytical performance model to represent the TORE in the case of heavy traffic. We demonstrate that SR-SWP yields a throughput restraint effect (TORE) in particular situations when packet losses occur. Hence, widely used reliable data-transfer protocols such as TCP-SACK and RLC utilize this sliding window mechanism in conjunction with a selective-repeat ARQ (automatic repeat request) function, namely, the selective-repeat sliding window protocol (SR-SWP). A sliding window mechanism is well known to be a convenient way to integrate cumulative acknowledgement and flow control functions in a simple manner.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
